In accounting, a general ledger is used to record a company’s ongoing transactions. Within a general ledger, transactional data is organized into assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and owner’s equity. After each sub-ledger has been closed out, the accountant prepares the trial balance.
- GL or General Ledger codes stand for numerical names that are given to accounts.Account #105, for example, could be the GL code for accounts receivable.
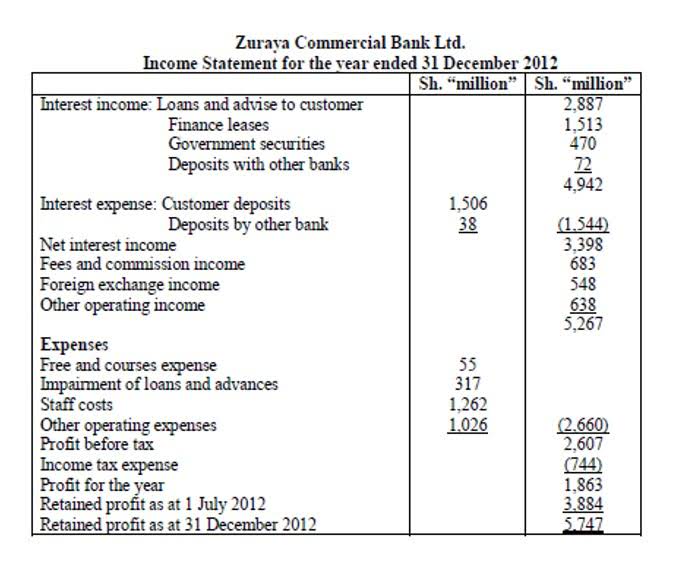
- So, the operating income includes sales revenue, income received as fees and commission, etc.
- Thus, as per the above table, the credit sales figure of $200,000 would go into the accounts receivable control account.
- When your business records revenue from sales, this will increase owner’s equity because it means that the company has earned more money.
Most accounting software will compile some of these ledgers while still letting you view them independently. Depending on the size of your business and what your business does, you might not need to use all of them. Create a journal or log with the transaction details as each transaction takes place.2. Categorization of the transactions under relevant accounts, i.e.; cash, sales, or accounts payable.3. Since the earliest times, the general ledger has been a cornerstone of good accounting. Before computerization, accountants literally ‘kept the books‘ by handwriting entries into massive ledgers, that was how businesses of all sizes kept track of every transaction.
General ledgers prepare a trial balance.
Accounting software can be a game-changer in this regard since it can streamline the process so general ledger reviews can be performed frequently. While most of these basics are applicable to any business, we also cover special considerations for law firms. Accounts payable is the money a company owes to its suppliers and vendors for products and services purchased on credit. When a company buys something from a vendor, it typically doesn’t pay for it immediately. This credit card is not just good – it’s so exceptional that our experts use it personally. It features a lengthy 0% intro APR period, a cash back rate of up to 5%, and all somehow for no annual fee!
Accounting 101 for Small Businesses
This is so because you do not want to understate expenses in your financial statements for the next 12 months. Some of these accounts are balance general ledger accounting services sheet accounts and some are income statement accounts. Furthermore, the assets are categorized into current assets and fixed assets.
Why Use a General Ledger?
Furthermore, all the accounting entries are transferred from the Journal to the Ledger. Now, each of your transactions follows a procedure before they are represented in the final books of accounts. First, the transactions are recorded in the Original Book of Entry, known as Journal. Once the Journal is complete, these transactions are then posted to individual accounts contained in General Ledger.
These transactions can occur across areas such as revenue, expenses, assets and liabilities. General ledgers also known as GL, are master financial statements that record all of your company’s financial Transactions. The accounts that are recorded in a General ledger include equity, expenses, assets, liabilities, and income or revenue. They provide an updated view of the company’s assets and liabilities, as well as how efficiently it manages cash.
How to Calculate and Increase Your Inventory Turnover Ratio
Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets. A legal practice should also be sure to implement the right internal controls for document retention and recordkeeping. These controls must be in place for legal matters, so be sure controls are implemented for the accounting department as well. Luke O’Neill writes for growing businesses in fintech, legal SaaS, and education.
You can save time on bookkeeping tasks with QuickBooks experts by your side. QuickBooks Online users have access to QuickBooks Live Assisted Bookkeeping, where experts provide guidance, answer questions, and show you how to do tasks in QuickBooks. Have more time to work on what you love when you spend less time on bookkeeping.